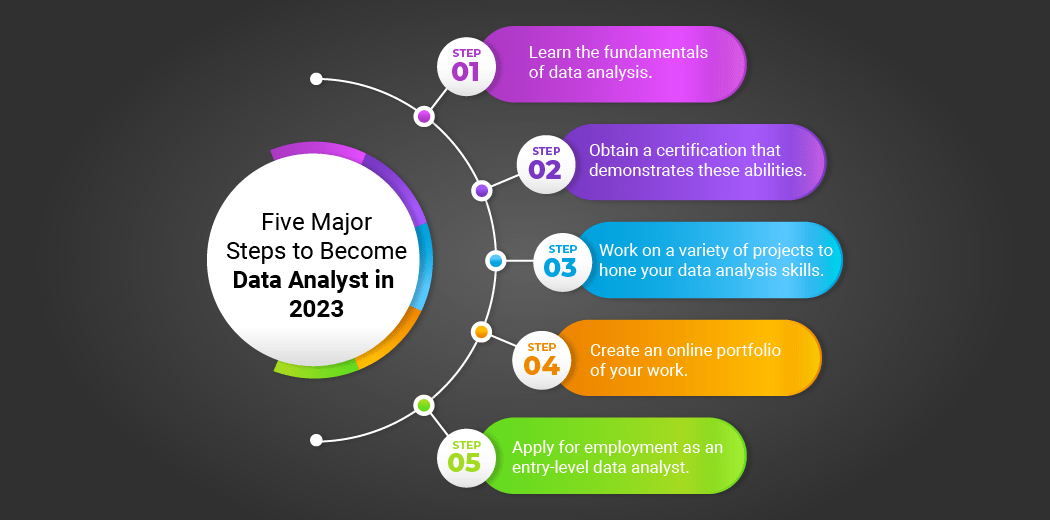
How To Become A Data Analyst: A Comprehensive Guide To A Rewarding Career
In today's data-driven world, the role of a data analyst has become increasingly important across various industries. Data analysts are responsible for interpreting complex data sets and providing actionable insights that drive business strategies and decision-making processes. With the rise of big data and the demand for data-driven decision-makers, more individuals are considering a career in data analysis. But where does one start on this path? How does one become a proficient data analyst? This article will guide you through the essential steps and skills needed to embark on this rewarding career journey.
The journey to becoming a data analyst involves acquiring a diverse set of skills, including technical expertise in data management, statistical analysis, and data visualization. Moreover, it requires a keen understanding of business principles and effective communication abilities to translate data-driven insights into business strategies. Aspiring data analysts must be prepared to engage in continuous learning and adaptation, as the field evolves with technological advancements and changes in data usage trends. This guide will provide a detailed roadmap, outlining the qualifications and skills necessary to succeed in this dynamic field.
Whether you're a recent graduate seeking your first role in data analysis, a professional aiming to transition into the field, or simply curious about what the role entails, this guide will offer valuable insights and practical advice. By the end of this article, you'll have a clearer understanding of the steps involved in becoming a data analyst, the skills that are in demand, and the resources available to help you on your journey. So, let's dive into the world of data analysis and explore how you can become a successful data analyst.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Role of a Data Analyst
- Education and Qualifications Required
- Essential Skills for Data Analysts
- Gaining Practical Experience
- Tools and Technologies Used in Data Analysis
- Building a Strong Portfolio
- Networking and Professional Development
- Certifications and Advanced Education
- Job Search Strategies and Interview Preparation
- Career Progression in Data Analysis
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Understanding the Role of a Data Analyst
The role of a data analyst is multifaceted, requiring a combination of technical expertise and business acumen. Data analysts are responsible for collecting, processing, and performing statistical analyses on large sets of data. They work closely with business stakeholders to identify data-driven opportunities for improvement and innovation. By transforming raw data into meaningful insights, data analysts help organizations make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and profitability.
At its core, the role of a data analyst involves data cleaning and preparation, exploratory data analysis (EDA), and the creation of data visualizations to communicate findings effectively. Data analysts must be proficient in using various data analysis tools and programming languages such as SQL, Python, and R. They often work in teams and collaborate with data scientists, engineers, and business analysts to ensure that data insights align with organizational goals and strategies.
Moreover, data analysts play a crucial role in storytelling through data. They must be able to communicate complex data findings in a clear and concise manner, making it accessible to non-technical stakeholders. This requires strong communication skills and a deep understanding of the business context in which they operate. As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven strategies, the demand for skilled data analysts continues to grow, making it a promising career choice for those interested in data and analytics.
Education and Qualifications Required
To become a data analyst, a solid educational foundation is essential. Most data analysts hold at least a bachelor's degree in a related field such as statistics, mathematics, computer science, or business administration. These programs typically cover the fundamental concepts of data analysis, including statistical methods, data management, and programming. Some universities also offer specialized degrees in data science or analytics, which provide a more focused curriculum on data-driven techniques and technologies.
In addition to formal education, many aspiring data analysts choose to pursue additional qualifications to enhance their skills and marketability. Online courses, workshops, and bootcamps offer a range of learning opportunities for individuals looking to gain hands-on experience and deepen their understanding of data analysis tools and techniques. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer courses in data analysis, ranging from beginner to advanced levels, covering topics such as Python programming, machine learning, and data visualization.
While formal education provides a strong foundation, practical experience and self-directed learning are equally important for aspiring data analysts. Building a portfolio of projects and engaging in internships or volunteer opportunities can provide valuable real-world experience and help demonstrate your skills to potential employers. Furthermore, staying updated with the latest trends and technologies in data analysis is crucial for continuous growth and development in this rapidly evolving field.
Essential Skills for Data Analysts
Data analysts require a diverse set of skills to excel in their roles. These skills can be broadly categorized into technical skills, analytical skills, and soft skills. Technical skills are essential for manipulating and analyzing data, while analytical skills are necessary for interpreting data and drawing meaningful insights. Soft skills, on the other hand, are crucial for effective communication and collaboration with team members and stakeholders.
Technical Skills
The technical skills required for data analysis include proficiency in programming languages such as SQL, Python, or R. SQL (Structured Query Language) is used for querying and managing databases, allowing data analysts to extract and manipulate data efficiently. Python and R are popular programming languages for data analysis, offering powerful libraries and tools for data manipulation, statistical analysis, and data visualization.
In addition to programming skills, data analysts must be familiar with data visualization tools such as Tableau, Power BI, or Google Data Studio. These tools enable data analysts to create interactive dashboards and visualizations that effectively communicate data insights to stakeholders. Knowledge of statistical analysis and data modeling techniques is also essential for data analysts to identify trends, patterns, and correlations within data sets.
Analytical Skills
Analytical skills are critical for data analysts to interpret data accurately and derive meaningful insights. These skills involve the ability to think critically, identify patterns, and solve complex problems using data-driven approaches. Data analysts must be able to conduct exploratory data analysis (EDA) to understand the underlying structure of data and identify potential biases or anomalies.
Data analysts also need strong quantitative skills to perform statistical analyses and evaluate the significance of data findings. This includes understanding concepts such as hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and data modeling. The ability to analyze data and draw conclusions based on evidence is essential for making informed decisions and providing actionable recommendations to stakeholders.
Soft Skills
Soft skills are equally important for data analysts, as they facilitate effective communication and collaboration with team members and stakeholders. Data analysts must be able to convey complex data insights in a clear and concise manner, tailoring their communication style to their audience. This requires strong presentation and storytelling skills, as well as the ability to create compelling visualizations that engage and inform stakeholders.
Furthermore, data analysts must be able to work collaboratively in cross-functional teams, often involving data scientists, engineers, and business analysts. Strong interpersonal and teamwork skills are essential for fostering positive working relationships and ensuring that data-driven insights align with organizational goals. Additionally, data analysts must be adaptable and open to learning, as the field of data analysis is constantly evolving with new technologies and methodologies.
Gaining Practical Experience
Practical experience is crucial for aspiring data analysts to build their skills and gain confidence in their abilities. There are several ways to gain practical experience, including internships, volunteer opportunities, and personal projects. These experiences allow individuals to apply their theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, develop their problem-solving skills, and build a portfolio of work that showcases their capabilities.
Internships
Internships provide valuable hands-on experience and exposure to the day-to-day responsibilities of a data analyst. Many companies offer internship programs for students and recent graduates, providing opportunities to work on data analysis projects under the guidance of experienced professionals. Internships not only help individuals gain practical experience but also provide networking opportunities and potential pathways to full-time employment.
When seeking internships, it's important to research companies and industries that align with your interests and career goals. Tailor your application materials to highlight your skills and enthusiasm for data analysis, and be prepared to demonstrate your ability to work with data through projects or coursework. Internships can be competitive, so it's essential to apply early and explore multiple opportunities.
Volunteer Opportunities
Volunteer opportunities offer another avenue for gaining practical experience in data analysis. Many nonprofit organizations and community groups rely on data to measure impact and make informed decisions, and they often seek volunteers with data analysis skills to assist with these efforts. Volunteering allows individuals to contribute to meaningful causes while developing their skills and gaining experience working with diverse data sets.
To find volunteer opportunities, reach out to local nonprofit organizations or search for online platforms that connect volunteers with organizations in need of data analysis support. Be clear about your skills and the type of experience you're seeking, and be open to learning and collaborating with others. Volunteering can be a rewarding way to gain practical experience while making a positive impact in your community.
Personal Projects
Personal projects are an excellent way for aspiring data analysts to explore their interests and develop their skills independently. Working on personal projects allows individuals to choose topics they're passionate about and experiment with different data analysis techniques and tools. Personal projects also provide an opportunity to showcase creativity and initiative, demonstrating to potential employers your ability to work independently and solve complex problems.
To start a personal project, identify a data set or topic that interests you and set clear objectives for what you want to achieve. Document your process and findings, and create visualizations or reports to communicate your insights. Share your projects on platforms like GitHub or a personal website to build your portfolio and demonstrate your skills to potential employers. Personal projects not only help you gain practical experience but also provide a platform for continuous learning and growth.
Tools and Technologies Used in Data Analysis
Data analysts rely on a variety of tools and technologies to perform their work efficiently and effectively. These tools facilitate data collection, cleaning, analysis, and visualization, enabling data analysts to derive insights and communicate findings to stakeholders. Familiarity with these tools is essential for aspiring data analysts to succeed in their roles and stay competitive in the job market.
Data Analysis Software
Data analysis software such as Microsoft Excel, SAS, and SPSS are commonly used by data analysts for data manipulation, statistical analysis, and reporting. Excel is widely used for its versatility and ease of use, offering a range of functions and features for data analysis and visualization. SAS and SPSS are specialized software for statistical analysis, providing advanced analytical capabilities and data management tools.
These software tools are essential for data analysts to perform tasks such as data cleaning, descriptive statistics, and regression analysis. Familiarity with these tools allows data analysts to efficiently process and analyze data, providing valuable insights to support decision-making processes.
Programming Languages
Programming languages such as Python, R, and SQL are critical tools for data analysts, enabling them to perform complex data manipulations and analyses. Python and R are widely used for their powerful libraries and packages for data analysis, machine learning, and data visualization. Python's libraries, such as Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib, provide comprehensive tools for data manipulation and visualization, while R's packages, such as ggplot2 and dplyr, offer advanced statistical analysis and visualization capabilities.
SQL is essential for querying and managing databases, allowing data analysts to extract and manipulate data efficiently. Proficiency in these programming languages is crucial for data analysts to perform advanced analyses, automate repetitive tasks, and create data-driven solutions.
Data Visualization Tools
Data visualization tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio are essential for creating interactive and engaging visualizations that communicate data insights effectively. These tools provide a range of features for creating charts, dashboards, and reports, allowing data analysts to present data in a visually appealing and accessible manner.
Familiarity with data visualization tools enables data analysts to create compelling visualizations that highlight key findings and trends, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and act on data insights. Visualization tools also facilitate data exploration and analysis, allowing data analysts to identify patterns and relationships within data sets.
Collaboration and Communication Tools
Collaboration and communication tools such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Trello are essential for data analysts to work effectively in cross-functional teams. These tools facilitate communication and collaboration, enabling data analysts to share insights, coordinate projects, and collaborate with team members and stakeholders.
Effective communication and collaboration are crucial for data analysts to ensure that data-driven insights align with organizational goals and strategies. Familiarity with these tools allows data analysts to work efficiently and collaboratively, contributing to the success of data analysis projects and initiatives.
Building a Strong Portfolio
A strong portfolio is an essential asset for aspiring data analysts, showcasing their skills, experience, and accomplishments to potential employers. A well-crafted portfolio demonstrates your ability to work with data, solve complex problems, and communicate insights effectively. It provides concrete evidence of your capabilities and sets you apart from other candidates in a competitive job market.
Showcasing Projects
Your portfolio should include a selection of projects that highlight your skills and expertise in data analysis. Choose projects that demonstrate your ability to work with different data sets, perform complex analyses, and create compelling visualizations. Include a variety of projects that showcase different aspects of your skills, such as data cleaning, exploratory data analysis, and data visualization.
For each project, provide a brief description of the objectives, methods, and results. Highlight any challenges you encountered and how you overcame them, and include visualizations or reports that illustrate your findings. Make sure to document your process and provide context for your work, demonstrating your ability to think critically and solve problems using data-driven approaches.
Creating a Personal Website
A personal website is an effective way to present your portfolio and showcase your skills to potential employers. A well-designed website provides a professional platform to display your projects, share your insights, and communicate your expertise in data analysis. It also allows you to control your online presence and make a strong impression on potential employers.
When creating a personal website, focus on clean design and user-friendly navigation. Include an "About Me" section that provides an overview of your background, skills, and interests, and a "Portfolio" section that showcases your projects. Consider adding a blog where you can share your thoughts on data analysis topics, industry trends, or recent projects, demonstrating your passion and expertise in the field.
Using Online Platforms
Online platforms such as GitHub, Kaggle, and LinkedIn offer additional opportunities to showcase your skills and connect with potential employers. GitHub is a valuable platform for sharing code and collaborating on projects, allowing you to demonstrate your programming skills and contribute to open-source projects. Kaggle provides opportunities to participate in data science competitions and collaborate with other data analysts, helping you gain practical experience and build your reputation in the data analysis community.
LinkedIn is an essential platform for networking and professional development, allowing you to connect with industry professionals, share your accomplishments, and stay informed about job opportunities. Make sure to keep your LinkedIn profile updated with your latest projects, skills, and achievements, and engage with the data analysis community by sharing insights, articles, and participating in discussions.
Networking and Professional Development
Networking and professional development are crucial for aspiring data analysts to advance their careers and stay informed about industry trends and opportunities. Building a strong professional network allows you to connect with industry experts, learn from their experiences, and gain insights into the data analysis field. Engaging in professional development opportunities helps you stay updated with the latest skills and knowledge, ensuring continuous growth and development in your career.
Attending Conferences and Workshops
Conferences and workshops provide valuable opportunities for networking and professional development. Attending industry events allows you to connect with other data analysts, share insights, and learn from experts in the field. These events often feature keynote speakers, panel discussions, and hands-on workshops, providing a wealth of knowledge and inspiration for your career.
When attending conferences and workshops, be proactive in networking and engaging with other attendees. Take advantage of networking sessions, social events, and online platforms to connect with industry professionals and expand your network. Follow up with new contacts after the event to maintain relationships and explore potential collaborations or job opportunities.
Joining Professional Organizations
Joining professional organizations related to data analysis and data science can provide valuable resources and support for your career development. Organizations such as the Data Science Society, the International Association for Statistical Education, and the Association for Computing Machinery offer networking opportunities, educational resources, and industry news to help you stay informed and connected.
Membership in professional organizations also provides access to conferences, workshops, webinars, and online communities, allowing you to engage with other data analysts and share your experiences. These organizations often offer certification programs, mentorship opportunities, and career resources to support your professional growth and development.
Participating in Online Communities
Online communities and forums provide a platform for data analysts to connect, share knowledge, and collaborate on projects. Platforms such as Reddit, Stack Overflow, and Data Science Central offer communities focused on data analysis and data science, where you can engage with other professionals, ask questions, and share insights.
Participating in online communities allows you to stay informed about industry trends, learn from others' experiences, and gain valuable insights into data analysis techniques and tools. Be active in these communities by contributing to discussions, sharing your knowledge, and learning from others. Engaging with online communities can help you build your reputation and expand your professional network.
Certifications and Advanced Education
Certifications and advanced education can enhance your credentials and demonstrate your commitment to continuous learning and professional development. Earning certifications in data analysis or related fields can validate your skills and knowledge, making you more competitive in the job market. Advanced education, such as a master's degree or specialized certification, can provide deeper insights and expertise in data analysis, opening up new career opportunities and pathways.
Data Analysis Certifications
Several organizations offer certifications in data analysis, providing a formal recognition of your skills and expertise. Certifications such as the Certified Analytics Professional (CAP), Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate, and Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate are widely recognized in the industry and demonstrate your proficiency in data analysis tools and techniques.
When choosing a certification, consider your career goals and the specific skills you want to develop. Research the requirements, exam format, and study materials for each certification, and invest time in preparing for the exam. Earning a certification not only enhances your credentials but also demonstrates your commitment to professional development and continuous learning.
Advanced Education Programs
Advanced education programs, such as master's degrees in data science or analytics, provide comprehensive training in data analysis techniques and tools. These programs often cover advanced topics such as machine learning, data mining, and big data technologies, providing a deeper understanding of data-driven methodologies and applications.
Pursuing advanced education can enhance your expertise and open up new career opportunities, such as roles in data science, data engineering, or data strategy. When considering advanced education, research programs that align with your career goals and offer a curriculum that meets your needs. Consider factors such as program length, format, and cost, as well as opportunities for networking and professional development.
Online Courses and Workshops
Online courses and workshops offer flexible and accessible learning opportunities for data analysts at all levels. Platforms such as Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer a wide range of courses in data analysis, covering topics such as data visualization, machine learning, and programming languages. These courses are often taught by industry experts and provide hands-on experience with real-world data sets and projects.
Online courses and workshops allow you to learn at your own pace and focus on specific skills or topics that interest you. They provide opportunities for continuous learning and skill development, helping you stay updated with the latest trends and technologies in data analysis. Many online courses also offer certificates of completion, which can enhance your credentials and demonstrate your commitment to professional development.
Job Search Strategies and Interview Preparation
Finding a job as a data analyst requires a strategic approach to job searching and interview preparation. In a competitive job market, it's essential to differentiate yourself from other candidates and demonstrate your skills and expertise in data analysis. Developing a strong resume, crafting a compelling cover letter, and preparing for interviews are crucial steps in the job search process.
Developing a Strong Resume
Your resume is your first opportunity to make a positive impression on potential employers. A well-crafted resume highlights your skills, experience, and accomplishments, demonstrating your qualifications for a data analyst role. When developing your resume, focus on showcasing your technical and analytical skills, as well as your ability to communicate and collaborate effectively.
Use clear and concise language, and tailor your resume to each job application by emphasizing the skills and experience that align with the job requirements. Include specific examples of projects or accomplishments that demonstrate your ability to work with data and solve complex problems. Highlight any certifications, education, or professional development achievements that enhance your credentials.
Crafting a Compelling Cover Letter
A cover letter provides an opportunity to introduce yourself to potential employers and explain why you're a strong candidate for the data analyst role. Use your cover letter to highlight your passion for data analysis, your relevant skills and experience, and your enthusiasm for the company and position. Tailor your cover letter to each job application, addressing the specific requirements and qualifications outlined in the job description.
Be concise and focused in your cover letter, and use specific examples to illustrate your skills and accomplishments. Demonstrate your understanding of the company's goals and values, and explain how your skills and experience align with their needs. A compelling cover letter can set you apart from other candidates and increase your chances of landing an interview.
Preparing for Interviews
Interview preparation is crucial for success in the job search process. Interviews provide an opportunity to demonstrate your skills and expertise, as well as your fit for the company and role. To prepare for interviews, research the company and the specific role you're applying for, and be ready to discuss your relevant skills and experience.
Practice answering common interview questions for data analyst roles, such as questions about your technical skills, problem-solving abilities, and experience working with data. Be prepared to discuss specific projects or accomplishments that demonstrate your skills and expertise, and use the STAR (Situation, Task, Action, Result) method to structure your responses.
Additionally, be prepared to ask thoughtful questions about the company and the role, demonstrating your interest and enthusiasm for the position. Practice your communication and presentation skills, as interviews often involve discussing data insights and explaining complex concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
Career Progression in Data Analysis
Career progression in data analysis offers a range of opportunities for growth and advancement, allowing data analysts to take on more complex and strategic roles within organizations. As you gain experience and expertise in data analysis, you may have the opportunity to progress into roles such as senior data analyst, data scientist, data engineer, or data strategy consultant. Understanding the potential career paths and opportunities for advancement can help you set goals and plan your career development.
Advancing to Senior Data Analyst Roles
As a senior data analyst, you'll take on more complex and strategic responsibilities, such as leading data analysis projects, mentoring junior analysts, and collaborating with cross-functional teams. Senior data analysts often have greater autonomy and influence in decision-making processes, using their expertise to drive data-driven strategies and initiatives.
To advance to a senior data analyst role, focus on developing your technical and analytical skills, as well as your leadership and communication abilities. Seek out opportunities to lead projects, contribute to strategic initiatives, and collaborate with stakeholders across the organization. Demonstrating your ability to drive results and provide valuable insights can help you progress to more senior positions.
Transitioning to Data Scientist Roles
Data scientists use advanced analytical techniques and machine learning algorithms to derive insights from complex data sets. Transitioning to a data scientist role often requires additional skills and expertise in areas such as machine learning, data mining, and big data technologies. Data scientists work on more complex and exploratory projects, using their expertise to develop predictive models and algorithms that inform business strategies.
To transition to a data scientist role, focus on developing your skills in machine learning, programming, and advanced statistical analysis. Consider pursuing additional education or certifications in data science or related fields, and seek out opportunities to work on data science projects or collaborate with data scientists. Building a strong foundation in data analysis and gaining practical experience in data science techniques can help you transition to this advanced role.
Exploring Data Engineering Roles
Data engineers are responsible for designing, building, and maintaining the infrastructure and systems that support data analysis and processing. Data engineers work closely with data analysts and data scientists to ensure that data is accessible, reliable, and efficient, enabling data-driven decision-making across the organization.
To explore data engineering roles, focus on developing your skills in data architecture, database management, and data warehousing. Familiarity with big data technologies such as Hadoop, Spark, and cloud computing platforms is also essential for data engineering roles. Gaining experience in data engineering projects and collaborating with data engineers can help you transition to this technical and strategic role.
Becoming a Data Strategy Consultant
Data strategy consultants work with organizations to develop and implement data-driven strategies and initiatives. They use their expertise in data analysis and business strategy to advise organizations on how to leverage data for competitive advantage and innovation. Data strategy consultants often work with senior leadership and stakeholders to align data initiatives with organizational goals and drive data-driven decision-making.
To become a data strategy consultant, focus on developing your skills in data analysis, business strategy, and stakeholder management. Building a strong understanding of industry trends and best practices in data-driven decision-making is essential for this strategic role. Consider gaining experience in consulting or strategic roles, and seek out opportunities to work with senior leadership on data-driven initiatives. Developing a strong reputation as a trusted advisor and thought leader in data strategy can help you succeed in this career path.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the typical career path for a data analyst?
Data analysts typically start in entry-level roles, working on data analysis projects and collaborating with cross-functional teams. As they gain experience and expertise, they may progress to senior data analyst roles, taking on more complex and strategic responsibilities. From there, they may transition to roles such as data scientist, data engineer, or data strategy consultant, depending on their skills and interests.
2. What skills are essential for a data analyst?
Essential skills for data analysts include technical skills such as proficiency in programming languages (e.g., SQL, Python, R), data analysis software (e.g., Excel, SAS, SPSS), and data visualization tools (e.g., Tableau, Power BI). Analytical skills, such as critical thinking and problem-solving, are crucial for interpreting data and deriving insights. Soft skills, such as communication and collaboration, are also important for effectively conveying data insights and working with stakeholders.
3. How can I gain practical experience as a data analyst?
You can gain practical experience as a data analyst through internships, volunteer opportunities, and personal projects. Internships provide hands-on experience and exposure to the day-to-day responsibilities of a data analyst. Volunteering with nonprofit organizations or community groups allows you to contribute to meaningful causes while developing your skills. Personal projects enable you to explore your interests and experiment with different data analysis techniques independently.
4. What are the best online courses for learning data analysis?
Several online platforms offer courses in data analysis, including Coursera, edX, and Udacity. These platforms offer a range of courses covering topics such as data visualization, machine learning, and programming languages. Some popular courses include "Data Science Specialization" on Coursera, "Introduction to Data Science" on edX, and "Data Analyst Nanodegree" on Udacity. Choose courses that align with your learning goals and provide hands-on experience with real-world data sets.
5. How important is networking for a data analyst's career?
Networking is crucial for a data analyst's career, as it provides opportunities to connect with industry experts, learn from their experiences, and gain insights into the field. Building a strong professional network can help you stay informed about industry trends, discover job opportunities, and collaborate on projects. Attend conferences, join professional organizations, and participate in online communities to expand your network and engage with the data analysis community.
6. What certifications are valuable for a data analyst?
Certifications such as the Certified Analytics Professional (CAP), Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate, and Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate are valuable for data analysts, as they demonstrate proficiency in data analysis tools and techniques. Earning a certification enhances your credentials and demonstrates your commitment to professional development. Choose certifications that align with your career goals and the specific skills you want to develop.
Conclusion
Becoming a data analyst is a rewarding and dynamic career choice, offering opportunities to work with data, solve complex problems, and drive data-driven decision-making. The journey to becoming a data analyst involves acquiring a diverse set of skills, gaining practical experience, and engaging in continuous learning and professional development. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you'll be well-equipped to embark on a successful career in data analysis.
Whether you're just starting your journey or looking to advance your career, remember that the field of data analysis is constantly evolving, and staying updated with the latest trends and technologies is crucial for success. Embrace the challenges and opportunities that come your way, and continue to learn and grow as a data analyst. With dedication, perseverance, and a passion for data, you can achieve your goals and make a meaningful impact in the world of data analysis.
For more information and resources on how to become a data analyst, consider exploring online platforms, attending industry events, and connecting with the data analysis community. By staying informed and engaged, you'll be well-positioned to succeed in this exciting and ever-evolving field.
Article Recommendations
- Wwwshophq
- Gainbridge Fieldhouse Player Crossword
- Evangeline Lilly Parents
- Lola Astanova Partner
- Z435 John Deere
- Shoeonhead Wedding
- Doll Dresses For Humans
- Shirtless Major League Baseball Players
- Alloy Forging Minecraft
- Yk Osiris And Diddy